In the realm of modern manufacturing, plastic extrusion has emerged as a pivotal technology across various industries, establishing its significance through a multitude of applications. Renowned expert Dr. John Wilson, a leading figure in materials engineering, once asserted, "Plastic extrusion is not just a process; it is the backbone of innovation in industries ranging from construction to automotive." This statement emphasizes the transformative power of plastic extrusion and its integral role in developing efficient solutions tailored to meet the ever-evolving demands of diverse markets.
The versatility of plastic extrusion allows for the creation of intricate shapes and profiles, making it an ideal choice for applications in sectors like packaging, consumer goods, and even healthcare. As industries continue to innovate and seek sustainable alternatives, plastic extrusion stands at the forefront, enabling manufacturers to reduce waste and enhance production efficiency. By understanding the top applications of plastic extrusion, stakeholders can better appreciate the impact of this technology on their respective fields and seize opportunities for growth and development.
Plastic extrusion is a versatile manufacturing process that involves the continuous shaping of thermoplastic materials. The process begins with the heating of plastic pellets until they reach a molten state. These molten plastics are then forced through a designed die to create specific shapes, which are subsequently cooled and solidified. This technique allows for the production of long lengths of uniform cross-section products, such as pipes, sheets, and profiles. The ability to produce these items in a continuous manner not only enhances efficiency but also reduces waste, making plastic extrusion an attractive option for various industries.
In addition to its efficiency, plastic extrusion is celebrated for its adaptability. It can accommodate a wide range of materials, including various polymers that can be modified or blended to achieve desired properties. This flexibility makes it suitable for applications across several sectors, such as construction, automotive, and consumer goods. For instance, in the construction industry, extruded plastic products are commonly used for insulation, cladding, and piping systems. By leveraging the unique characteristics of different plastics, manufacturers can create specialized products that meet specific performance standards, thus broadening the applications of plastic extrusion in the marketplace.
Plastic extrusion is a versatile manufacturing process employed across various industries, utilizing an array of materials tailored to meet specific needs. One of the primary materials used in plastic extrusion is polyethylene (PE), known for its excellent chemical resistance and durability. This makes it a preferred choice in packaging applications, such as plastic bags and film, where flexibility and strength are essential.
Another widely used material is polypropylene (PP), recognized for its lightweight properties and high melting point, making it ideal for producing automotive components and consumer goods.
In addition to PE and PP, polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is frequently utilized in plastic extrusion for its rigidity and weather resistance. This material is commonly found in construction applications, particularly for pipes and siding. Furthermore, thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) are employed when flexibility and rubber-like properties are required, often used in products that need to withstand dynamic bending and stretching.
The choice of materials in plastic extrusion significantly influences the performance and longevity of the final products, making it critical for manufacturers to select the right type based on their application and environmental conditions.
Plastic extrusion is a pivotal manufacturing process utilized across a wide range of industries. One of the primary sectors leveraging this technique is the construction industry, where plastic profiles are extruded for windows, doors, and other structural components. According to a report by Market Research Future, the global plastic extrusion market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.5% from 2020 to 2027, driven largely by the increasing demand for lightweight and durable building materials. The ability to create custom shapes and sizes through extrusion allows for enhanced flexibility in design, making it an attractive option for architects and builders alike.
Another significant industry adopting plastic extrusion is the packaging sector. The versatility of extruded plastics allows for the production of various packaging solutions, including films, sheets, and containers. A study by Smithers Pira estimates that the global plastic packaging market will reach $1 trillion by 2024, with extrusion technologies playing a crucial role in meeting this surging demand. The process's efficiency and ability to produce high-volume materials at lower costs make it an indispensable component in developing sustainable packaging solutions, as companies increasingly focus on reducing waste and enhancing recyclability.
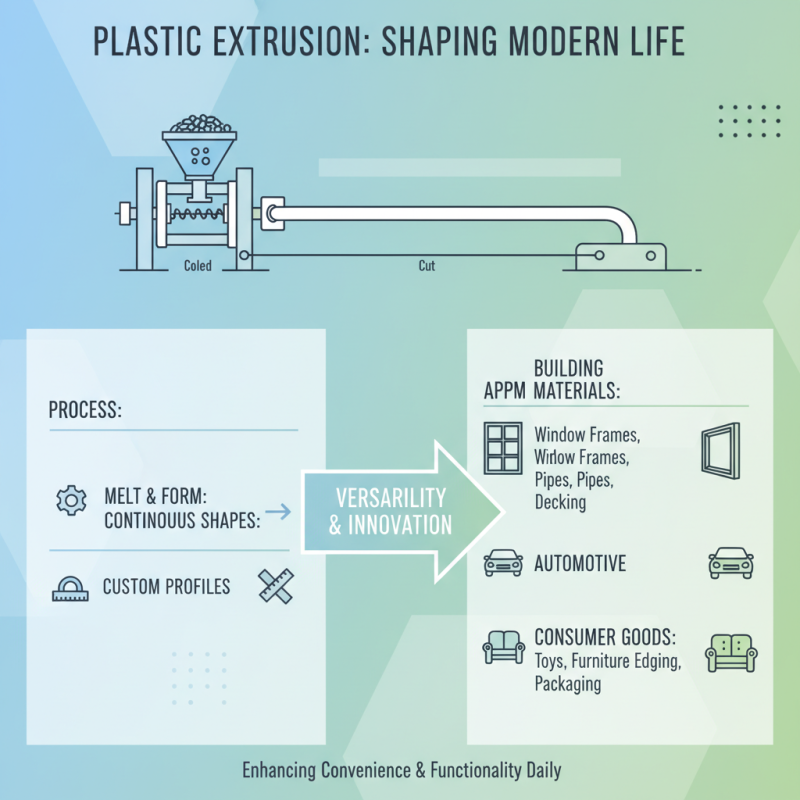
Plastic extrusion is a versatile manufacturing process that has significantly influenced various aspects of daily life. Through this innovative technique, continuous lengths of plastic are shaped and formed into useful items that enhance convenience and functionality in everyday scenarios. From the sleek profiles used in window frames to complex piping systems, the applications of plastic extrusion are omnipresent in residential and commercial settings alike.
One of the most innovative applications of plastic extrusion is in the production of packaging materials. Extruded films and sheets provide lightweight, durable options that help protect products while minimizing waste. Additionally, in the realm of textiles, plastic extrusion contributes to the creation of functional fibers used in clothing and upholstery, offering benefits such as moisture-wicking and UV protection. Moreover, in the construction industry, the extrusion process allows for the design of custom-based insulation materials that enhance energy efficiency in buildings, showcasing the transformative impact of plastic extrusion on sustainable living.
The future of plastic extrusion is poised for significant advancements, driven by the growing demand for sustainable and efficient manufacturing processes. With an increasing emphasis on recycling and minimizing environmental impact, industries are exploring innovative materials that can be extruded more efficiently. Biodegradable plastics and bio-based polymers are at the forefront, presenting exciting opportunities that not only reduce waste but also offer new functionalities in products.
Technological advancements in automation and the integration of Industry 4.0 principles are also shaping the future of plastic extrusion. Smart manufacturing systems are enabling real-time monitoring and optimization of extrusion processes, thus increasing productivity and consistency while reducing costs. Additionally, the implementation of advanced simulation tools allows manufacturers to predict material behavior during the extrusion process more accurately, leading to enhanced design capabilities and reduced time-to-market for new products. As these trends continue to evolve, they will significantly impact various industries, enhancing product versatility and sustainability in plastic extrusion applications.
This chart illustrates the top applications of plastic extrusion across various industries, highlighting their significance and estimated market share in percentage terms.